Thrombin Generation (PPP, PRP, WB)
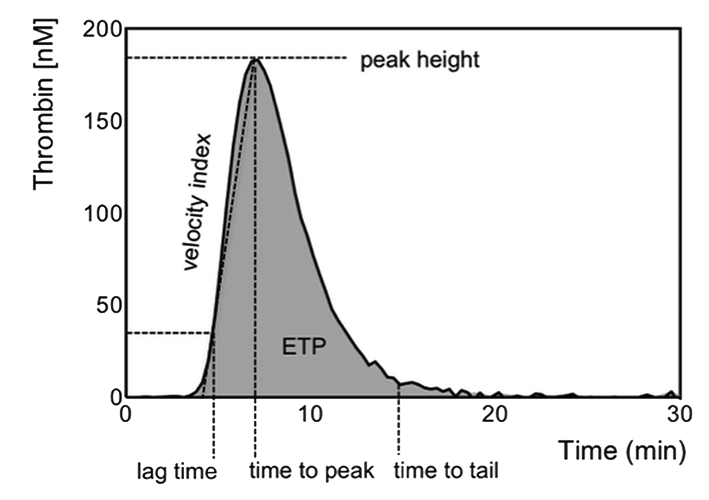
The lag time is the time needed to form the first traces of thrombin, the ETP represents the total amount of active thrombin formed during thrombin generation and the peak height the maximal amount of thrombin formed.
Numerous articles have shown that an increased thrombin generation is associated with thrombosis, whereas a decrease in thrombin generation is associated with bleeding.
Thrombin generation by means of the CAT assay can be used for several applications, including:
- To monitor the use of antithrombotic therapy, e.g. treatment with direct oral anticoagulants (e.g. Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban), vitamin K antagonists (e.g. warfarin), heparins (e.g. unfractionated heparin, low molecular weight heparin) and antiplatelet drugs (e.g. Clopidogrel)
- To support the development of antithrombotic drugs, such direct inhibitors of thrombin or FXa
- To determine the coagulation state of patients at increased risk of thrombosis or bleeding
- To monitor patients with hemophilia, such as treatment with FVIII concentrates or treatment with FVIIa (NovoSeven)
- To measure genetic and acquired thrombotic disorders, e.g. deficiency in antithrombin (AT)
- To determine thrombogenic capacity of materials
- To quantify the levels of coagulation factors in low sample volumes
- To elucidate coagulation mechanisms
Thrombin generation triggered with tissue factor can be measured in platelet poor plasma (PPP), platelet rich plasma (PRP) and whole blood. The conditions of the thrombin generation assay can be modified to better accommodate the question at hand. For example, the addition of thrombomodulin to the trigger allows to include the contribution of the protein C pathway to thrombin generation.
Reference values for hemostatic parameters
Thrombin generation in plasma and whole blood has been used as a research tool in the field of thrombosis and hemostasis. There is substantial evidence that thrombin generation can be used to elucidate coagulation mechanisms, investigate hemorrhagic coagulopathies, predict the risk of (recurrent) thrombosis, and to monitor hemostatic and antithrombotic therapy. Thrombin generation has not reached clinical application, partly due to lack of reference values.
The assessment of platelet (dys)function is of crucial relevance in several clinical settings, including monitoring the response to antiplatelet treatment, evaluation of perioperative haemostasis, transfusion medicine and identification of bleeding disorders. The current gold standard to test platelet function for the diagnosis of bleeding disorders is light transmission aggregometry (LTA). However, LTA is laborious, relatively insensitive to small changes in platelet function and the outcome is affected by haemolysis and an abnormal platelet count. Additionally, the test is poorly standardized, consumes large blood volumes and requires skilled technicians in specialized laboratories. We developed a user-friendly, reliable and quick flow cytometric based assay to determine platelet function in whole blood. Our assay uses three different platelet agonists (TRAP, CRP and ADP) and two platelet activation markers (αIIbβ3 receptor activation and P-selectin expression).
For clinical applicability of hemostatic tests, it is of great importance to determine reference values in healthy individuals. Therefore, we determined references ranges for thrombin generation in platelet poor plasma (PPP), platelet rich plasma (PRP) and whole blood and for whole blood platelet function in 129 healthy individuals according to CLSI (Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute) guidelines.
References:
Bloemen S, Huskens D, Konings J, Kremers R, Miszta A, de Laat B, Kelchtermans H. Interindividual variability and normal ranges of whole blood and plasma thrombin generation. JALM. 2017 Sept; 2 (2): 150 -164.
Huskens D, Sang Y, Konings J, van der Vorm L, de Laat B, Kelchtermans H, Roest M. Standardization and reference ranges for whole blood platelet function measurements using a flow cytometric platelet activation test. PLoS One. 2018 Feb 1;13(2):e0192079.


