Scientific research is an important activity of Synapse. The research topics of Synapse are: antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), haemostasis and bleeding, haemostasis and thrombosis and measurement of haemostasis medication. We educate PhD students, master students and bachelor students in the state of the art developments in haemostasis research.
Antiphospholipid Syndrome
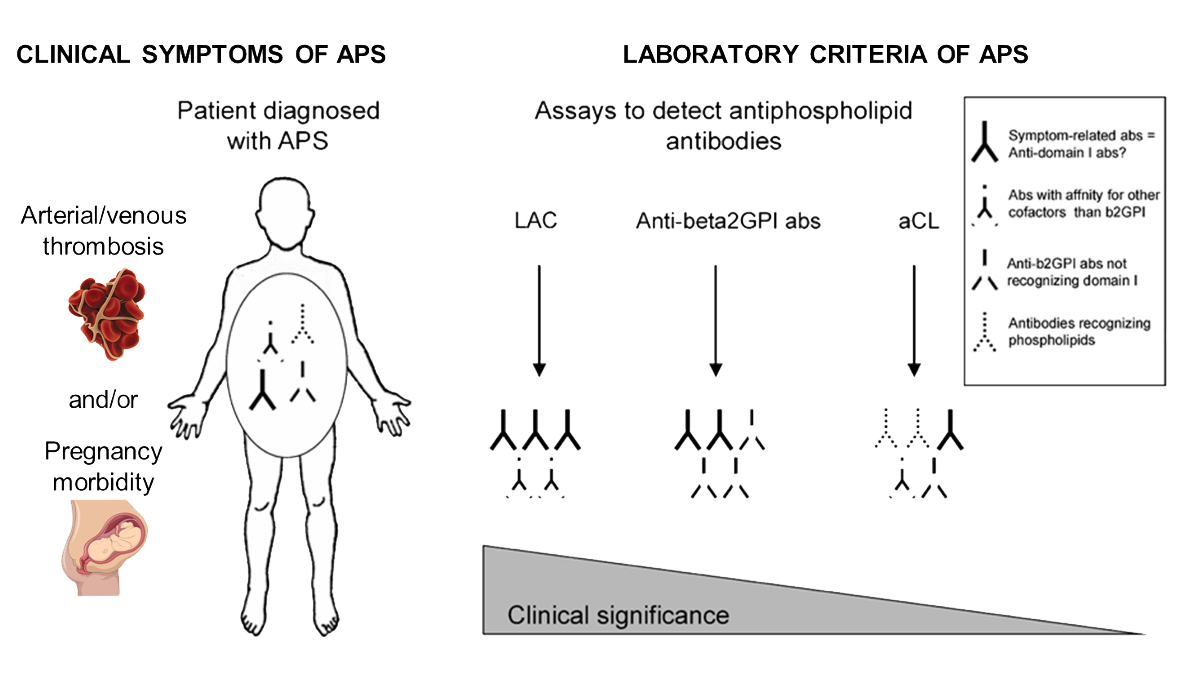
Patients with persistent anti-phospholipid (aPL) antibodies and thrombosis or pregnancy-related morbidity are diagnosed with the autoimmune disorder antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). Official classification criteria for APS recognize three distinct, but overlapping aPL populations: antibodies against the phospholipid (PL)-binding protein β2-glycoprotein I (β2GPI), antibodies against β2GPI bound to cardiolipin and antibodies that prolong clotting times in a PL-dependent manner; so called lupus anticoagulant (LAC)
Reference values for haemostasis parameters
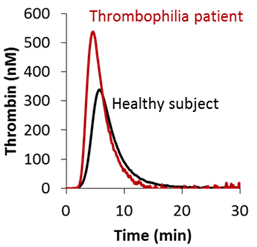
The development proces from a promising innovative haemostasis test to a clinical diagnostic device is a long procedure. A very important step in this development is to determine the distribution of the test outcomes in healthy volunteers, who are representative for the general population. Synapse Research Institute has done several of those reference studies to determine the reference ranges of thrombin generation and of a flow cytometry based platelet activation test (PACT).
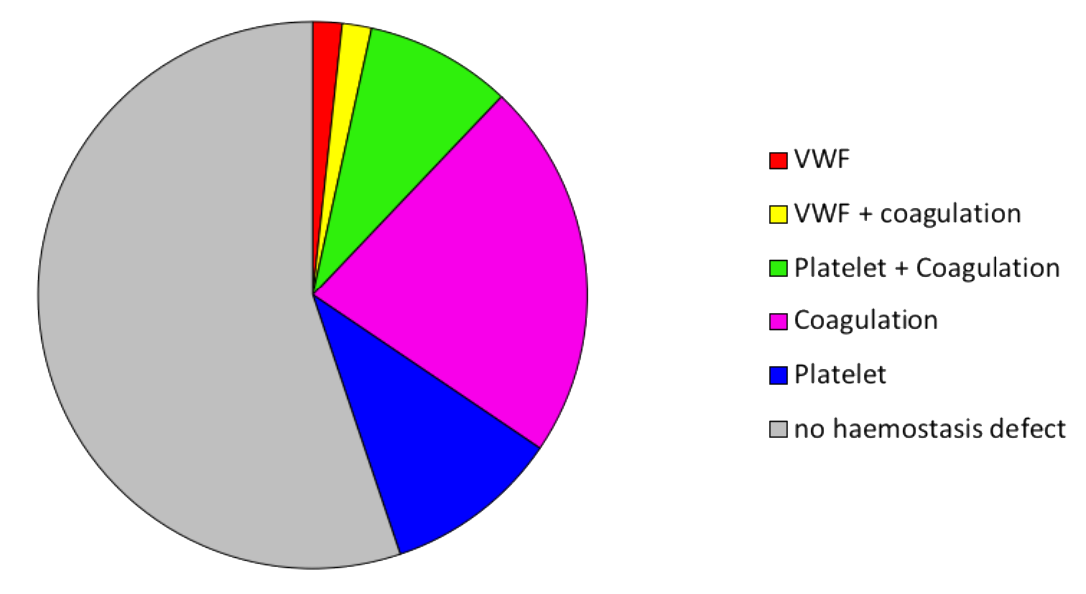
Haemostasis and bleeding
Thrombocytopenia, defined as a platelet count below 150 ×109/L, impairs hemostasis and may result in bleeding complications. Thrombocytopenia can develop due to infectious causes (sepsis, chronic liver disease) or immunologic causes (Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP), acute respiratory distress syndrome). Furthermore, it is a common complication of open heart surgery, which is associated with bleeding risks and increased mortality.
Measurement of haemostasis medication
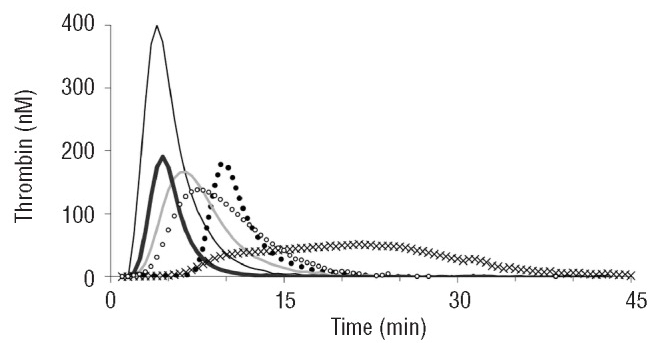
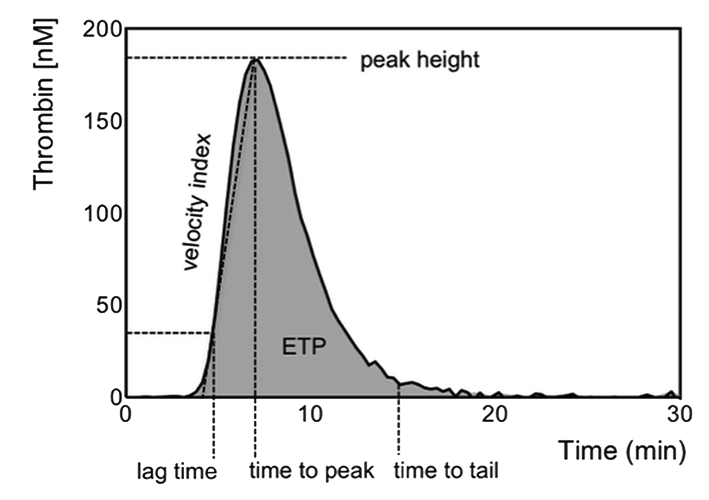
Calibrated automated thrombinography (CAT) is a sensitive method to assess the coagulation phenotype of individual patients, as it globally measures the bleeding tendency and the thrombosis tendency in individuals. In addition, Synapse has developed a TG based test to simultanuously measure the DOAC concentrations in blood